- GPS based toll collection announced by Indian Minister of Road Transport and Highways, Shri Nitin Gadkari.
- Expected to reduce vehicle stoppage time on Toll Booths.
- Satellite accuracy in question.
Announcement by MoRTH Shri Nitin Gadkari
Union Minister Nitin Gadkari’s recent announcement marks a significant advancement in India’s toll collection methodologies, introducing GPS-based systems to the forefront. This innovative step is expected to revolutionize the way tolls are collected, making the process more efficient and less time-consuming.
How Does GPS Toll Collection Work?
GPS toll collection utilizes satellite technology to track vehicles as they travel on toll roads. Through this system, tolls are automatically calculated based on the vehicle’s movement, detected via GPS devices installed in vehicles. This method eliminates the need for physical toll booths, thereby reducing traffic congestion and enabling smoother flow on highways.
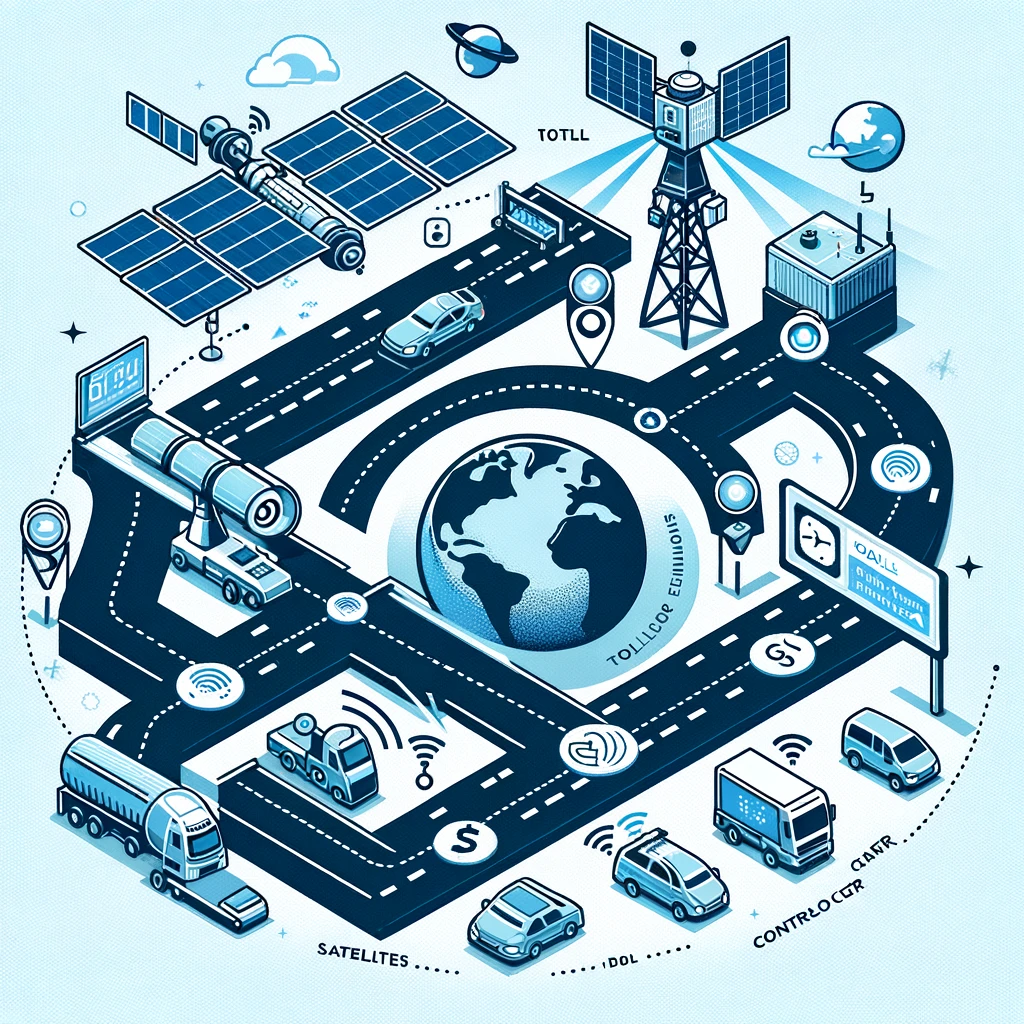
Satellite-Based Toll Systems Explained
In this system, a satellite tracks a GPS device inside the vehicle and deducts tolls when the vehicle passes through any toll gate.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of how it works:
- GPS Devices in Vehicles: Vehicles are equipped with GPS devices that can communicate with satellites. These devices continuously transmit the vehicle’s location, speed, and direction of travel.
- Satellites in Orbit: A network of satellites continuously receives signals from the GPS devices in vehicles. These satellites are part of the Global Positioning System, orbiting the Earth and providing precise location data.
- Data Transmission to Control Center: The satellites relay the location data from vehicles to a control center on the ground. This data includes the specific routes taken by the vehicles on the toll roads.
- Toll Calculation: The control center processes the received data to calculate the toll charges based on the distance traveled on the toll road. The system can accurately determine the entry and exit points of the vehicle on the toll road, enabling a fair and precise toll charge.
- Billing and Payment Processing: Once the toll is calculated, the charge is automatically billed to the vehicle owner’s registered account. This could be linked to a bank account, credit card, or a pre-paid toll account. The payment is processed electronically, and the transaction is completed without any need for the vehicle to stop or physically interact with a toll booth.

Advantages
This system significantly reduces congestion at toll plazas, as vehicles do not need to stop for toll collection.
I expect the maximum stoppage time could be around 10-15 seconds per vehicle.
It also allows for a more efficient use of roadways, as the toll charges can be dynamically adjusted based on the distance traveled, type of vehicle, and time of day.
Furthermore, it offers a transparent and user-friendly method of toll collection, as users can track their toll charges and payments in real time.
Disadvantages
The satellite-based toll collection system, while innovative and efficient, also presents several disadvantages:
- High Implementation Costs: Establishing a satellite-based toll collection system requires significant initial investment in technology, infrastructure, and satellite communications. This includes the cost of equipping vehicles with GPS devices, setting up a central processing facility, and maintaining the satellite network.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of GPS devices to track vehicle movements raises privacy issues. There is a concern about how the data is stored, used, and protected. Users may be apprehensive about being constantly monitored, and there are valid worries regarding the potential misuse of location data.
- Dependence on Technology: Satellite-based systems rely heavily on the proper functioning of GPS devices, satellite networks, and data processing centers. Any technical failures, such as satellite disruptions, GPS device malfunctions, or system hacks, can lead to inaccuracies in toll collection or even system-wide outages.
- Weather and Environmental Impact: Satellite signals can be affected by severe weather conditions or obstacles like tunnels and tall buildings, potentially leading to inaccurate toll calculations or loss of tracking in certain areas.
- Equity and Accessibility Issues: Not all vehicle owners may have access to or can afford GPS devices, potentially leading to equity issues. This could result in certain segments of the population being disadvantaged or excluded from using toll roads, or facing higher costs if alternative toll collection methods are more expensive.
- Complexity in Dispute Resolution: Disputes over toll charges may be more complicated to resolve due to the automated nature of the system. Proving or disputing a journey’s details might require extensive data analysis and could lead to longer resolution times.
- Maintenance and Operational Costs: Ongoing maintenance of the technology and infrastructure, including updates to GPS devices and the central processing system, incurs continuous costs. Additionally, as technology advances, systems may need significant upgrades, further increasing expenses.
- Satellite Accuracy: The satellite accuracy may also affect the toll collection. Suppose you are not using the toll road, but you are using the free service road near it. If the satellite accuracy is bad in that area, the satellite might show that you were using the toll road.
Exploring Other Toll Collection Methods
In addition to the cutting-edge GPS and satellite-based systems, other traditional and electronic methods remain in use:
- Cash Payments: The oldest form of toll collection, where travelers pay toll charges in cash. While declining in popularity, it remains an option for those without access to digital payment methods. After the introduction of fast-tags in India, the charges for cash-based tolls have been doubled
- FASTag: A widely adopted electronic toll collection system in India, FASTag uses RFID technology to automatically deduct toll charges from a prepaid or linked bank account as vehicles pass through toll plazas.
- Vehicle Number Based Toll Collection: An innovative approach where cameras capture vehicle license plates at toll plazas, and toll charges are billed to the vehicle owner. This method offers an alternative for vehicles not equipped with FASTag or GPS devices.

